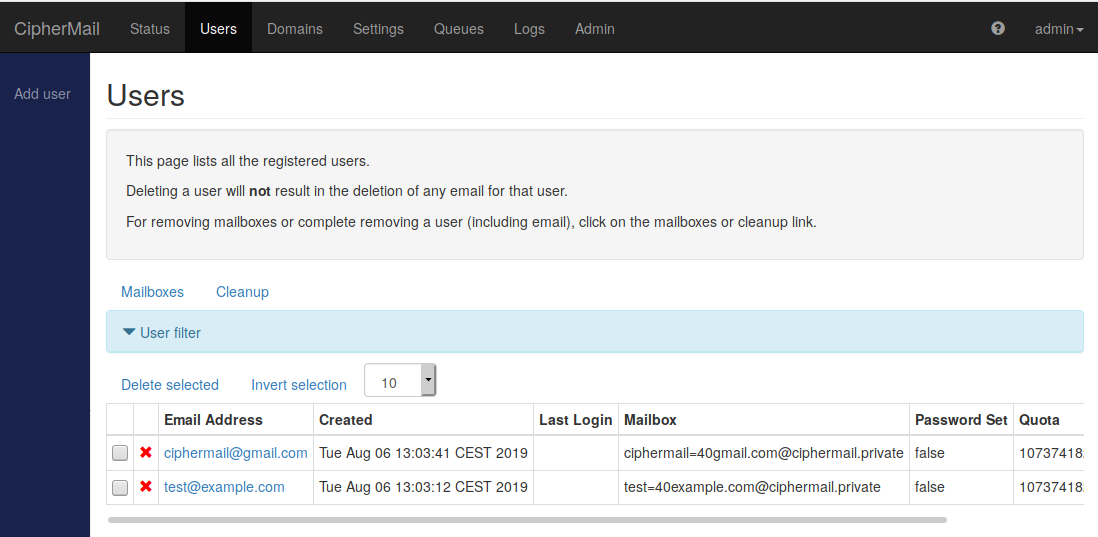
Users
The users page shows all users for which there is a mailbox. Webmail Messenger will automatically add a new user object the first time an email is sent to the user.
A user can be deleted by clicking the “red cross” icon or by selecting the user and then clicking Delete selected
Note
Deleting a user object does not result in the removal of the users mailbox. After a re-sign up, the user has access to all old emails. To completely delete all email for a user, remove the complete mailbox.
Mailbox
Email for a user is stored in the users mailbox. The available mailboxes can be listed and managed by clicking Mailboxes on the “Users” page. On the “Mailboxes” page, the available mailboxes will be shown. The following mailbox details will be listed: “Disk usage”, “Email”, “Mailbox”
Note
Only 10 mailboxes will be shown at the same time. Use the mailbox filter to search for specific mailboxes.
- Disk usage
The total disk size of the mailbox. The total size of the mailbox is limited by the quota for the user.
The email address associated with the mailbox.
- Mailbox
The directory where the mailbox is stored (as a sub directory of
/var/vmail/).
Note
Deleting a mailbox only deletes the email of that user. The login account is however not removed.
Mailbox filter
The mailbox filter can be used to search for specfic mailboxes.
- Hide active mailboxes
If “Hide active mailboxes” is set, only mailboxes will be shown for which the password is set. This can be used to remove mailboxes for users which never logged in.
User cleanup
For every Webmail Messenger user, a user object and mailbox is created. Email for a Webmail Messenger user is stored on the file system. To make sure that Webmail Messenger does not run out of disk space, it’s advised to periodically remove user accounts and mailboxes of users who haven’t logged in for a long time.
On the “User cleanup” page, users who have never logged or for which the last login has been some time ago can be deleted. Filtered users can be deleted by selecting the user and clicking “delete” selected.
Tip
The “User cleanup” page can be used to remove users and the associated inboxes. It is possible to configure Webmail Messenger to periodically delete old email for a user. This helps to prevent running out of disk space. See Auto cleanup for more information.
- Created
This field can be used to only show users which were created within a certain date range.
- Last login
This field can be used to only show users for which the “last login” field is set within a certain date range.
- Last login should not be set
If set, only users will be shown who never logged in.
- Password should not be set
If set, only users will be shown for which no password was set.
Domains
If an inherited setting should be explicitly set or modified for a domain, a domain object should be created. In most setups, there is no reason to add a domain.
Settings
Location
The name of the sub-directory, under /var/vmail/, where the email for the user is stored.
Disk usage
The total disk size in bytes of the user mailbox.
Quota
The current disk quota for the user.
Created
The date the user object was created.
Last login
The last login date of the user. Set to never if the user never logged in.
Password is set
If visible, a password is set for the user. The administrator can change the user password by clicking Change password.
Password is not set
If visible, a password is not yet set for the user. The administrator can set the user password by clicking Set password.
General
Comment
The comment field is a free form field which can be used to add comments for the settings. For example some brief explanation why certain settings have been changed for a domain.
Default portal login action
The “Default portal login action” determines which page is opened after the user logged in. The following options can be selected: Portal, Webmail (the default).
Use notification sender
If set, the initial sign-up email and the “new email” notification messages will be sent using the configured “Notification sender” as the sender, i.e., the “from” header and the envelope sender will be set to the email address configured under “Notification sender”.
If “Use notification sender” is set, the envelope sender is changed to the email address configured under “Notification sender” and the from header is rewritten to:
"in name of [email protected]" <notification@ciphermail.com>
where test@example.com is the original sender address and notification@ciphermail.com is the address configured under “Notification sender”.
If “Use notification sender” is not set, the initial sign-up email and the “new email” notifications from header and envelope sender address will be set to the same value as the original email.
Login allowed
If selected, the user is allowed to login. This can be used to temporarily disallow a user to login without having to remove the user account.
Relay recipient
This is the email recipient address to which the tunnelled S/MIME message will be sent from the CipherMail gateway. “Relay recipient” must match the “Webmail recipient” setting configured on the CipherMail gateway. It is advised to use the value configured by the initial setup wizard.
Portal base URL
The base URL for the user sign-up and password reset pages. This should normally be set to the fully qualified domain name (or IP address) of the server.
Example:
https://webmail.ciphermail.com
Notification sender
If “Use notification sender” is enabled, the from and envelop sender of the sign-up email and “new email” notifiction emails will be set to the value configured under “Notification sender”.
Webmail error recipient
If an email cannot be handled by the gateway, for example the email from the gateway is not correctly signed, a notification email to the “Webmail error recipient” will be sent.
Portal password policy
The portal password policy, defines the minimal requirements for a password selected by the end-user.
Note
The password policy is only enforced when the end-user configures the portal password, not when the administrator sets the portal password for a user.
The portal password policy should be configured as a JSON string using the following syntax:
{m: INT, r:[{p:REGEX}, {p:REGEX}, .... ]}
INT is a positive integer > 0 and REGEX is a regular expression.
m is the minimal number of patterns that should match for the password to be valid and r is a list of password rules (regular expressions). If m is not specified, the default value 1 will be used.
The password validator works as follows:
A password is matched against every rule (the regular expression) and if the number of matches is greater or equal to the minimal number of matches (as defined by the m parameter), the password is accepted.
Example regular expressions
The following regular expression will match if the password contains at least 8 characters:
.{8,}
The following regular expression will match if the password contains at least one lowercase character:
[a-z]
The following regular expression will match if the password contains at least one uppercase character:
[A-Z]
The following regular expression will match if the password contains at least one digit:
[0-9]
The following regular expression will match if the password contains at least one special character from the list @#$%^&+=
[@#$%^&+=]
The above examples can be combined to form more complex rules
Example policy rules
The following password policy will check whether the password is at least 8 characters long:
{r:[{p:'^.{8,}$'}]}
Note
^ and $ are strictly speaking not needed for the above regular expression.
The following password policy will check whether the password is at least 8 characters long, contains at least one lowercase character, at least one uppercase character and at least one digit:
{m:4, r:[{p:'.{8,}'}, {p:'[a-z]'}, {p:'[A-Z]'}, {p:'[0-9]'}]}
N out of M policy*
In the above example, the minimal patterns to match (the m parameter) was equal to the number of patterns. This means that every pattern should match before the password is accepted.
The minimal patterns to match can be set to a lower value if you want to have a policy which says that the password is accepted if at least N patterns match out of the possible M patterns.
Warning
if the minimal patterns to match (the m parameter) is set to a lower value than the number of possible patterns, make sure that every pattern at least defines minimal number of characters otherwise a short password might be accepted because the N out M rule might skip the minimal length pattern. For example the following rule is unsafe {m:1, r:[{p:'.{8,}'}, {p:'[a-z]'}]} because the password is accepted if only one pattern matches and therefore a single character lowercase password will match. Whem m is less than the number of patterns, at least specify the minimal length for every rule.
Example N our of M policy rules
The following password policy will check whether the password is at least 8 characters long or is 6 characters long and contains at least a special character from the list:
{m:1, r:[{p:'.{8,}'}, {p:'(?=.*[@#$%^&+=]).{6,}'}]}
Portal password policy URL
If configured, a link to the configured page will be added to the page on which the end-user can set the portal password. The URL should link to the page explaining the password policy.
Initial login allowed
By default, a user is allowed to login after signing up. By disabling “Initial login allowed”, the user is allowed to sign-up but not allowed to login after signing up.
Tip
“Initial login allowed” can be used for additional security. The first email sent to an external user allows the user to sign-up and read the email. If the first email however is sent to the wrong recipient, the recipient might have access to the sensitve email. By disabling “Initial login allowed”, the recipient is allowed to sign-up but not allowed to login. The sender of the email should then use additional means to check whether the correct recipient has signed-up and then enable the login for the user by selecting “Login allowed” for the user account.
Server secret
The “Server secret” is used to protect external resources against tampering (using the HMAC algorithm). For example the sign-up link in the sign-up message is protected to make sure that a recipient cannot change the URL. A global server secret will be automatically generated the first time the server starts. The server secret is a required setting. In most setups there is no need to override the inherited server secret.
Client secret
The “Client secret” is used for generating one time passwords for a recipient. A “Client secret” is automatically generated if needed.
Signup link validity
The number of minutes a sign-up link is valid.
Password reset link validity
The number of minutes a password reset link is valid.
Webmail
Webmail enabled
If set (the default), the user is allowed to open the Webmail inbox. If not set, the user is allowed to login into the portal (assuming that “Login allowed” is set) but is not allowed to open the Inbox.
This setting is used if you only want to use Webmail Messenger for PDF encryption.
Read receipt
If set, a read receipt will be sent when the user opens the email for the first time.
Rewrite reply sender
By default, a reply from a Webmail user is sent with the envelope sender and from address set to the real email address of the user.
If “Rewrite reply sender” is set, the envelope sender is changed to the email address configured under “Reply sender address” and the from header is rewritten to:
"in name of [email protected]" <reply-sender-address@ciphermail.com>
where test@example.com is the original sender address and reply-sender-address@ciphermail.com is the address configured under “Reply sender address”.
Tip
“Rewrite reply sender” should be used if the SMTP server which receives the reply emails, i.e., the SMTP server defined in “Webmail relay host”, contains anti-spoof or anti-spam checks (for example SPF or DKIM checks).
Send new mail notification
If “Send new mail notification” is set (the default), a “new mail” notification email will be sent to the user if a new mail is available. If “Send new mail notification” is not set, a notification email will not be sent.
Tip
“Send new mail notification” can be disabled if the recipient wants to keep it “secret” that the recipient has a Webmail Messenger account. If “Send new mail notification” is disabled, the recipient however needs to periodically login to check whether there are new emails.